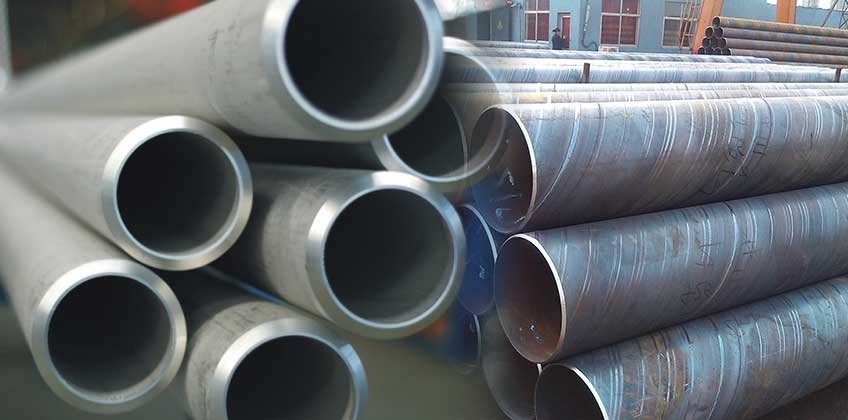
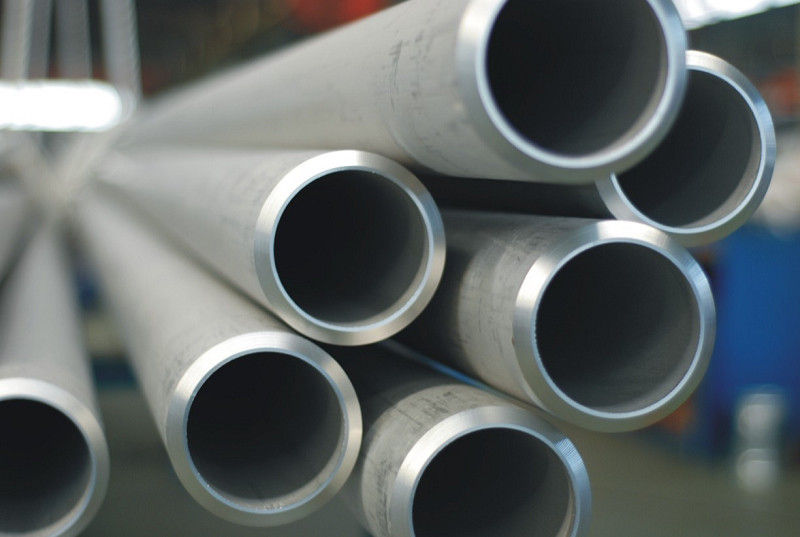
Seamless pipe and welded pipe are two common types of steel pipes used in a wide range of applications, including oil and gas pipelines, plumbing systems, and industrial processes.
Seamless pipe is made by drawing a solid steel billet or a hollow tube through a piercing rod to create a seamless pipe with a uniform diameter and thickness. It does not have any welded seam, making it more durable and reliable than welded pipes. Seamless pipes are often used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications due to their strength and resistance to corrosion.
Welded pipe, on the other hand, is made by welding two or more pieces of steel together using various welding techniques such as electric resistance welding (ERW), submerged arc welding (SAW), and fusion welding. Welded pipes are typically cheaper to produce than seamless pipes, but they may be weaker and more prone to corrosion due to the heat-affected zones created during the welding process.
Here's a table comparing the characteristics of seamless and welded pipes:
| Characteristic | Seamless Pipe | Welded Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Drawn from solid steel billet or hollow tube | Welded from two or more pieces of steel |
| Weld Seam | No weld seam | Has a visible weld seam |
| Strength | Stronger and more reliable due to uniform thickness and absence of weld seam | May be weaker due to heat-affected zones created during welding process |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly resistant to corrosion due to lack of weld seam | May be more prone to corrosion due to presence of weld seam and heat-affected zones |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to manufacturing process | Generally cheaper due to manufacturing process |
| Applications | Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications where reliability and durability are critical | Suitable for low-pressure and low-temperature applications that do not require high strength and corrosion resistance |
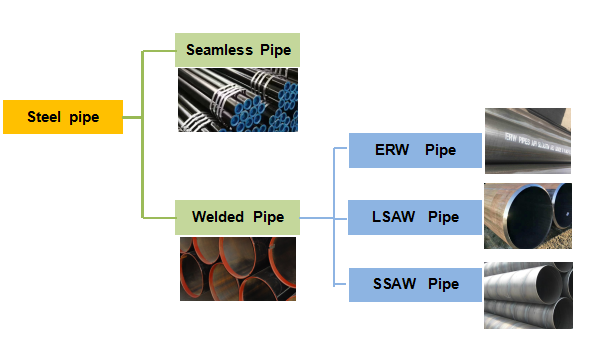
Seamless, SAW, ERW, and EFW are different types of pipes used in various applications. Here are the differences between these types of pipes:
Seamless Pipe: Seamless pipes are made from solid round steel billets that are heated and then stretched over a series of mandrels to create the desired shape and size of the pipe. Seamless pipes do not have any welding joints, and they are typically used in high-pressure applications such as oil and gas pipelines, refineries, and power plants.

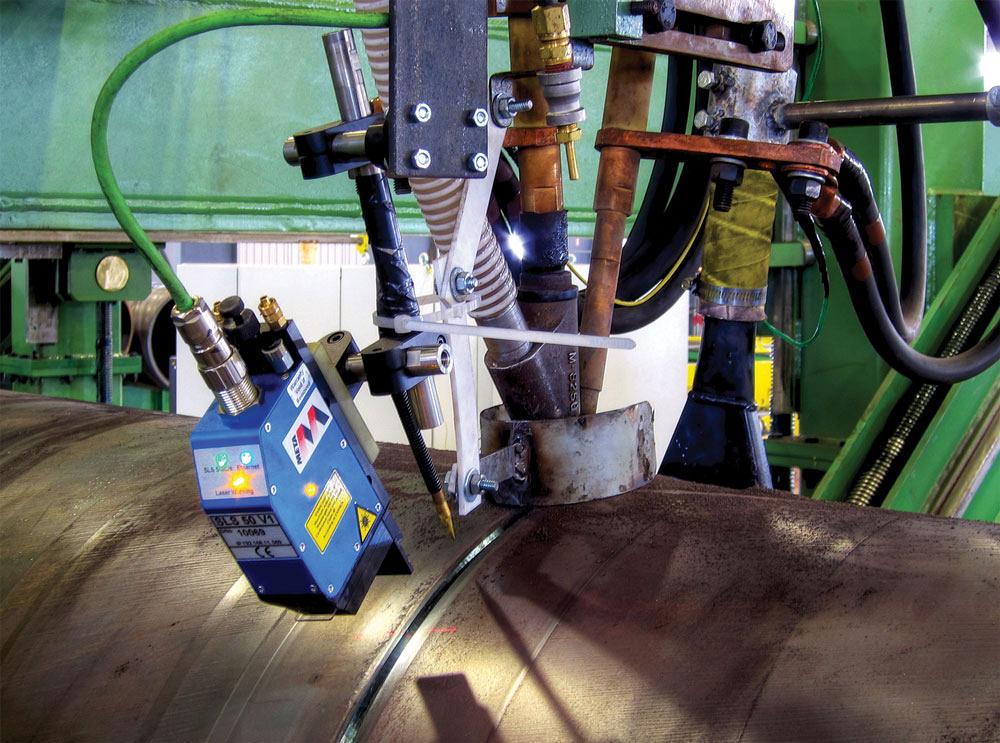
SAW Pipe: SAW stands for Submerged Arc Welding. SAW pipes are made by welding the edges of steel plates together to form a tubular structure. The welding process is done under a layer of granular flux, which protects the weld from contamination. SAW pipes are typically used in heavy-duty applications such as oil and gas pipelines, water pipelines, and structural applications.

ERW Pipe: ERW stands for Electric Resistance Welding. ERW pipes are made by rolling a strip of steel into a tubular shape and then welding the edges together using a high-frequency electric current. ERW pipes are typically used in low to medium-pressure applications such as water pipelines, gas pipelines, and plumbing.
EFW Pipe: EFW stands for Electric Fusion Welding. EFW pipes are made by melting the edges of two pieces of steel together using an electric arc. The melted edges are then pressed together to form a seamless bond. EFW pipes are typically used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications such as chemical plants, power plants, and nuclear reactors.

In summary, seamless pipes are made from solid round steel billets, SAW pipes are made by welding steel plates together, ERW pipes are made by welding a strip of steel into a tubular shape, and EFW pipes are made by melting the edges of two pieces of steel together using an electric arc. The choice of pipe type depends on the application and the required properties of the pipe, such as strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
Here are some general specifications for Seamless, SAW, ERW, and EFW pipes:
Pipe Type | Full Name | Production Method | Diameter Range | Wall Thickness Range | Length Range | Common Applications |
Seamless | Seamless Pipe | Hot rolling or cold drawing | 1/8" - 36" | 1.6mm - 60mm | Up to 12m | High-pressure, high-temperature applications in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation |
SAW | Submerged Arc Welded Pipe | Submerged arc welding | 16" - 100" | 6mm - 25mm | Up to 12.2m | Used for conveying low-pressure fluids such as water, gas, and oil in industries such as construction and agriculture |
ERW | Electric Resistance Welded Pipe | Electric resistance welding | 1/2" - 24" | 1.65mm - 20mm | Up to 18m | Used for conveying low-pressure fluids and for structural applications in industries such as construction and automotive |
EFW | Electric Fusion Welded Pipe | Electric fusion welding | 6" - 100" | 3.2mm - 25mm | Up to 12.2m | Used for conveying corrosive or high-temperature fluids in industries such as chemical and petrochemical |
Note: The above information is not exhaustive and there may be additional specifications for each type of pipe depending on the specific application and industry requirements.
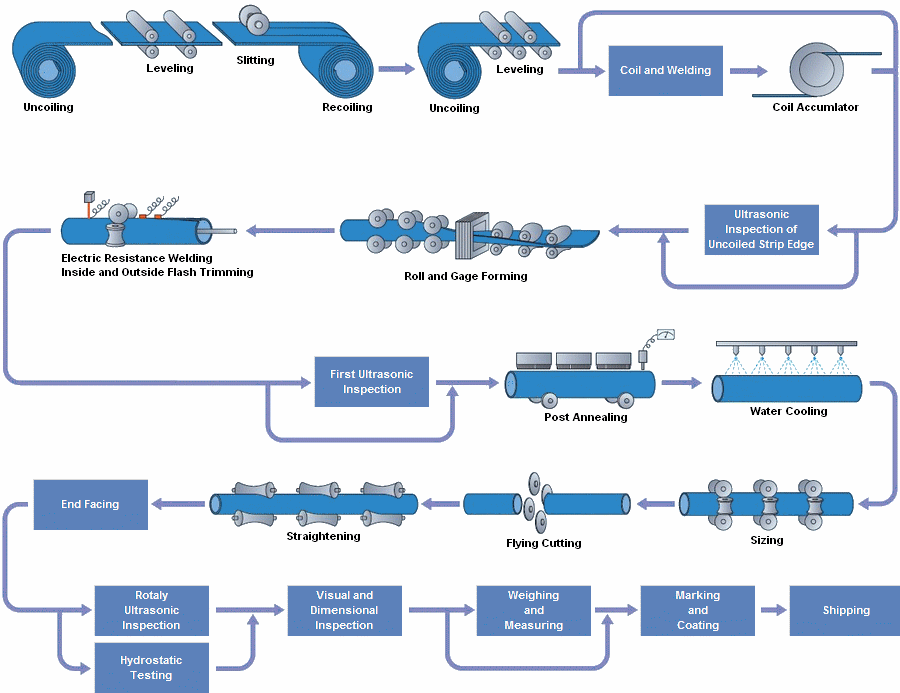
Spiral welded pipe is a type of steel pipe that is made by forming a spiral seam along its length using a continuous spiral welding process. The process involves a number of steps:
Coil Preparation: The first step in the process is to prepare the steel coils that will be used to make the pipe. The coils are inspected for defects and then trimmed to the required size and weight.
Uncoiling: The steel coils are then uncoiled and fed into the spiral welding machine.
Forming: The steel strip is formed into a cylindrical shape by passing it through a series of rollers.
Welding: As the strip is formed, a continuous spiral seam is welded along its length using either a submerged arc welding (SAW) or a Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) process.
Weld Inspection: The weld seam is inspected using ultrasonic or radiographic methods to ensure that it meets the required quality standards.
Pipe Cutting: The welded pipe is then cut to the required length using a saw or plasma cutting machine.
End Preparation: The ends of the pipe are beveled or squared off as required.
Testing: The finished pipe is subjected to various tests such as hydrostatic testing, mechanical testing, and non-destructive testing to ensure that it meets the required quality standards.
Coating and Marking: The final step in the process involves coating the pipe with a protective layer and marking it with the required identification and quality control information.
The spiral welding process is efficient and cost-effective, making it an ideal choice for the production of large diameter pipes used in the oil and gas, water, and construction industries.
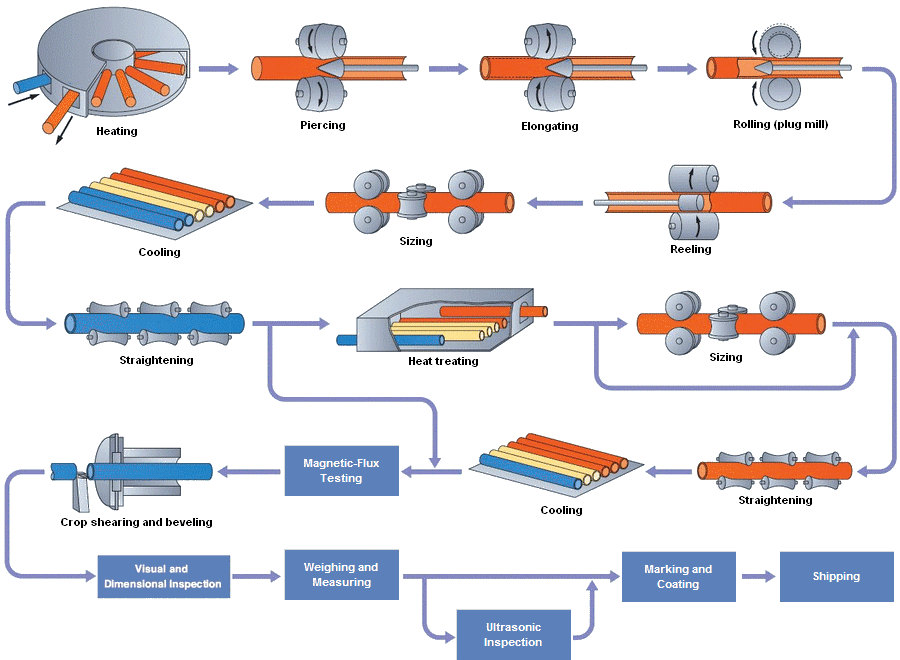
Seamless pipes are made by piercing a solid cylindrical billet of steel and then drawing it out into a hollow tube without any welding or seams. The process involves the following steps:
Billet Preparation: The first step in the process is to prepare the solid cylindrical billet of steel. The billet is heated to a high temperature to make it malleable.
Piercing: The billet is then pierced with a mandrel to create a hollow shell. The mandrel is a rod that is placed inside the billet to support the inner surface of the tube.
Rolling: The pierced billet is then rolled to reduce its diameter and wall thickness. This process is called the "reducing process," and it is repeated several times until the desired diameter and wall thickness are achieved.
Sizing: The rolled pipe is then sized to its final dimensions by passing it through a series of sizing rollers.
Heat Treatment: The seamless pipe is then heat-treated to improve its mechanical properties. This involves heating the pipe to a specific temperature and then cooling it down slowly to achieve the desired properties.
Cutting and Finishing: The final step in the process is to cut the seamless pipe to the required length and finish it with a variety of treatments, such as straightening, end facing, and chamfering.
Seamless pipes are used in a variety of applications, including oil and gas exploration, drilling, and transportation, as well as in the construction and automotive industries. The seamless pipe manufacturing process produces pipes with a high degree of uniformity and consistency, which makes them highly reliable and durable.
When ordering steel pipes, the nominal pipe size (NPS) and the wall thickness are the two most important measurements (schedule). Single random length (SRL) pipes can be 5–7 metres long, while double random length (DRL) pipes can be 11–13 metres long. Long pipelines can have lengths that are made to order. Ends of pipes can be bevelled, plain, threaded, threaded and coupled, or grooved.
Details of a typical order:
Type (Seamless or welded) (Seamless or welded)
The types of Nominal Pipe Size Schedule End
Material Grades
How many metres or feet?
Ssmsteel can help you get the steel pipe you need for any project. We are proud to offer a variety of high-quality steel products, such as seamless, ERW, LSAW, and SSAW pipes. We have a large network of reliable manufacturers in Australia and around the world, which lets us sell steel products at prices that are competitive. We also help our customers with financing and delivery, so they can get a full-service solution from us.
Contact us if you need to find steel pipe, and our friendly staff will help you through the whole process.
Contact us today at 8619527792928 or sales@ssmsteel.com
Contact: Sino Special Metal Co., Ltd.
Phone: 86-19527792928
E-mail: sales@ssmsteel.com
Whatsapp:86-19527792928
Add: Mudu town Jinfeng South Road, Wuzhong District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province
We chat
