People use pipe and tube interchangeably and think they mean the same thing. But pipe and tube are not the same thing in a lot of ways.
Here's the short answer:
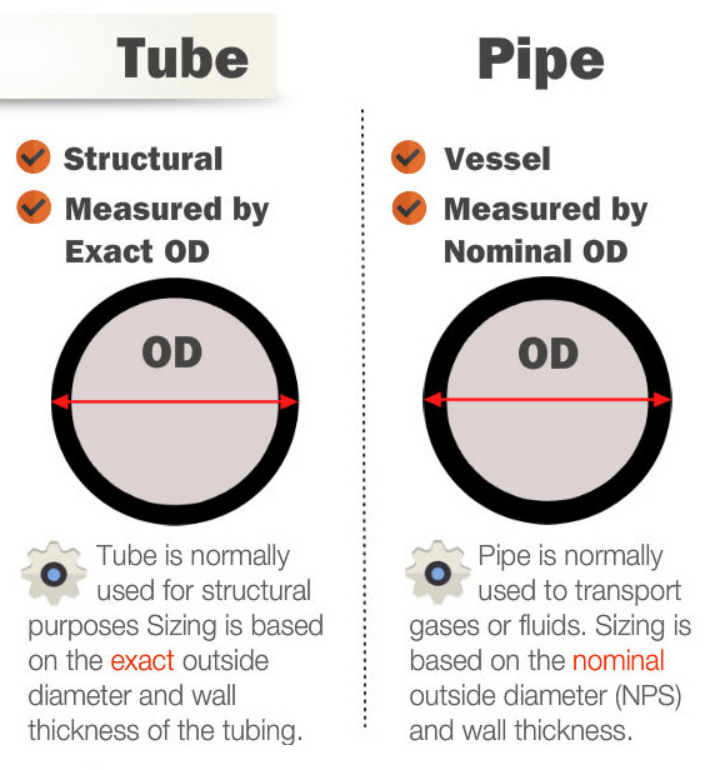
A TUBE is a round, square, rectangular, or oval hollow section measured by its outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness (WT), which are given in inches or millimeters. A PIPE is a round tube used to move fluids and gases. It is given a nominal pipe size (NPS or DN) that gives a rough idea of how much it can move.
Pipe is a hollow section with a round cross section that is used to move products. Fluids, gas, pellets, powders, and more are among the products.
The outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness are the most important measurements for a pipe (WT). The inside diameter (ID) of a pipe is equal to OD minus 2 times WT (schedule), which tells you how much liquid the pipe can hold.
Examples of actual O.D. and I.D.
Actual outside diameters
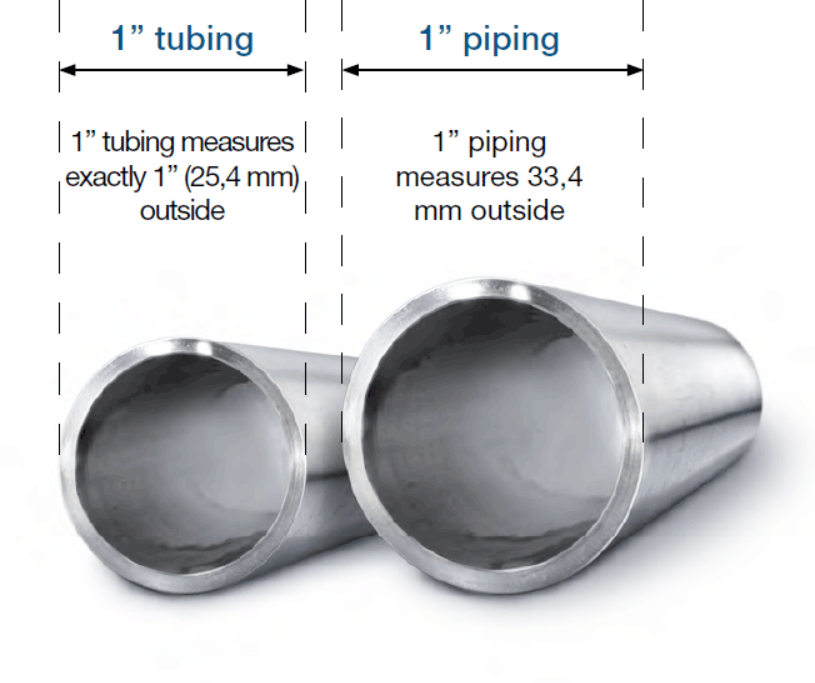
NPS 1 actual O.D. = 1.5/16" (33.4 mm)
NPS 2 actual O.D. = 2.3/8" (60.3 mm)
NPS 3 actual O.D. = 3.1/2" (88.9 mm)
NPS 4 actual O.D. = 4.1/2" (114.3 mm)
NPS 12 actual O.D. = 12.3/4" (323.9 mm)
NPS 14 actual O.D. = 14" (355.6 mm)
Actual inside diameters of a 1 inch pipe.
NPS 1-SCH 40 = O.D.33,4 mm - WT. 3,38 mm - I.D. 26,64 mm
NPS 1-SCH 80 = O.D.33,4 mm - WT. 4,55 mm - I.D. 24,30 mm
NPS 1-SCH 160 = O.D.33,4 mm - WT. 6,35 mm - I.D. 20,70 mm
Such as above defined, the inside diameter is determined by the oudside diameter (OD) and wall thickness (WT).
The most important mechanical parameters for pipes are the pressure rating, the yield strength, and the ductility.
The ASME B36.10 and ASME B36.19 specs cover the standard combinations of pipe Nominal Pipe Size and Wall Thickness (schedule) (respectively, carbon and alloy pipes, and stainless steel pipes).
The word "TUBE" is used to describe hollow sections that are round, square, rectangular, or oval and are used for pressure equipment, mechanical applications, and instrumentation systems.
The outside diameter and wall thickness of a tube are given in inches or millimeters.
PIPE vs TUBE | STEEL PIPE | STEEL TUBE |
Key Dimensions (Pipe and Tube Size Chart) | The most important dimensions for a pipe is the outer diameter (OD) together with the wall thickness (WT). OD minus 2 times WT (SCHEDULE) determine the inside diameter (ID) of a pipe, which determines the liquid capacity of the pipe. The NPS does not match the true diameter, it is a rough indication | The most important dimensions for a steel tube are the outside diameter (OD) and the wall thickness (WT). These parameters are expressed in inches or millimeters and express the true dimensional value of the hollow section. |
Wall Thickness | The thickness of a steel pipe is designated with a "Schedule" value (the most common are Sch. 40, Sch. STD., Sch. XS, Sch. XXS). Two pipes of different NPS and same schedule have different wall thicknesses in inches or millimeters. | The wall thickness of a steel tube is expressed in inches or millimeters. For tubing, the wall thickness is measured also with a gage nomenclature. |
Types of Pipes and Tubes (Shapes) | Round only | Round, rectangular, square, oval |
Production range | Extensive (up to 80 inches and above) | A narrower range for tubing (up to 5 inches), larger for steel tubes for mechanical applications |
Tolerances (straightness, dimensions, roundness, etc) and Pipe vs. Tube strength | Tolerances are set, but rather loose. Strength is not the major concern. | Steel tubes are produced to very strict tolerances. Tubulars undergo several dimensional quality checks, such as straightness, roundness, wall thickness, surface, during the manufacturing process. Mechanical strength is a major concern for tubes. |
Production Process | Pipes are generally made to stock with highly automated and efficient processes, i.e. pipe mills produce on a continuous basis and feed distributors stock around the world. | Tubes manufacturing is more lengthy and laborious |
Delivery time | Can be short | Generally longer |
Market price | Relatively lower price per ton than steel tubes | Higher due to lower mills productivity per hour, and due to the stricter requirements in terms of tolerances and inspections |
Materials | A wide range of materials is available | Tubing is available in carbon steel, low alloy, stainless steel, and nickel-alloys; steel tubes for mechanical applications are mostly of carbon steel |
End Connections | The most common are beveled, plain and screwed ends | Threaded and grooved ends are available for quicker connections on site |
Contact: Sino Special Metal Co., Ltd.
Phone: 86-19527792928
E-mail: sales@ssmsteel.com
Whatsapp:86-19527792928
Add: Mudu town Jinfeng South Road, Wuzhong District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province
We chat
